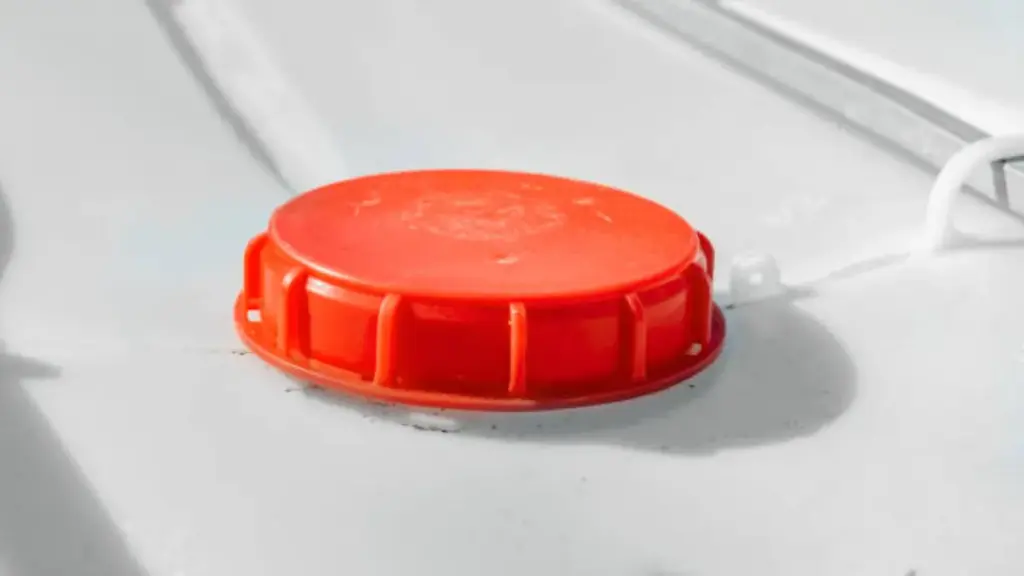
نما الطلب على الأغطية البلاستيكية الصناعية بشكل مطرد حيث تعطي الصناعات الأولوية للسلامة, متانة, والامتثال التنظيمي. في قطاعات مثل تخزين المواد الكيميائية, براميل الوقود, ومواد التشحيم الصناعية, تعتبر الأغطية الموثوقة ضرورية لمنع التسربات والحفاظ على سلامة المنتج. تستكشف هذه المقالة المواد, عملية التصنيع, ومعايير الجودة وراء الأغطية البلاستيكية عالية الأداء.
ما هي المواد المستخدمة لصنع الأغطية البلاستيكية?

يعد اختيار المادة المناسبة أمرًا أساسيًا لضمان قوة الغطاء البلاستيكي, متانة, والمقاومة الكيميائية. مواد مختلفة تناسب التطبيقات الصناعية المختلفة, والمواد المضافة يمكن أن تزيد من تعزيز الأداء. هنا لمحة مفصلة:
المواد الرئيسية
- البولي ايثيلين عالي الكثافة (حزب الشعوب الديمقراطيه): HDPE هي المادة الأكثر استخدامًا للأغطية الصناعية. إنه يوفر صلابة عالية, مقاومة كيميائية ممتازة, ويمكنه تحمل درجات الحرارة من -40 درجة مئوية إلى 120 درجة مئوية. إنه مثالي لبراميل الوقود, براميل كيميائية, وغيرها من الحاويات الثقيلة.
- مادة البولي بروبيلين (ص): يوفر PP مرونة أعلى ومقاومة حرارية, يتحمل درجات حرارة تصل إلى 140 درجة مئوية. غالبًا ما يتم استخدامه لعمليات التعبئة الساخنة, البيئات المعرضة للأشعة فوق البنفسجية, والتطبيقات التي تتطلب قبعات مرنة قليلاً.
أنواع البلاستيك الأخرى
- البولي ايثيلين (بي, بما في ذلك البولي إثيلين المنخفض الكثافة): مرنة وخفيفة الوزن, مناسبة للحاويات الصغيرة أو الأغطية ذات متطلبات الضغط المنخفض.
- بولي فينيل كلوريد (بولي كلوريد الفينيل): صعب, مقاومة كيميائيا, ولكنها أقل تحملاً للحرارة. يشيع استخدامها في زجاجات المختبر أو الأغطية الصناعية التي لا تتحمل درجات الحرارة العالية.
- أكريلونتريل بوتادين ستايرين (ABS): مقاومة تأثير قوية, تستخدم أحيانًا للقبعات عالية القوة, ولكنها أقل مقاومة للمواد الكيميائية من HDPE أو PP.
- البولي (جهاز كمبيوتر): شفاف ومقاوم للصدمات, بشكل أساسي لنوافذ المراقبة أو الأغطية المتخصصة.
- مادة البولي أميد (السلطة الفلسطينية, نايلون) و بولي أوكسي ميثيلين (بوم): قوة عالية ومقاومة التآكل, مناسبة للأغطية ذات النوع اللولبي أو ذات المتطلبات الميكانيكية, عادة في التطبيقات المخصصة.
إضافات مشتركة
- مثبتات الأشعة فوق البنفسجية: حماية ضد أشعة الشمس ومنع الهشاشة.
- وكلاء مكافحة ساكنة: تقليل تراكم الكهرباء الساكنة للسوائل القابلة للاشتعال أو الحساسة.
- ماستر: تتم إضافته بكميات محددة لتحقيق اللون المطلوب مع الحفاظ على الخصائص الفيزيائية للبلاستيك, مناسبة لتحديد العلامة التجارية أو الدفعة.
- معززات مقاومة للمواد الكيميائية: تحسين الأداء باستخدام المواد الكيميائية العدوانية.
فيما يلي جدول ملخص للرجوع إليه بسرعة:
| نوع البلاستيك | الميزات الرئيسية | التطبيقات النموذجية / استخدام الصناعة |
| البولي إثيلين عالي الكثافة (البولي ايثيلين عالي الكثافة) | صلابة عالية, مقاومة كيميائية ممتازة, نطاق درجة الحرارة -40 درجة مئوية إلى 120 درجة مئوية | براميل الوقود, براميل كيميائية, مواد التشحيم, حاويات صناعية ثقيلة |
| ص (مادة البولي بروبيلين) | مرن, مقاومة حرارية جيدة تصل إلى 140 درجة مئوية, مقاومة للأشعة فوق البنفسجية | حاويات التعبئة الساخنة, تخزين خارجي, براميل كيميائية تتطلب مرونة |
| بي (البولي ايثيلين, بما في ذلك البولي إثيلين المنخفض الكثافة) | خفيف الوزن, مرن, صلابة أقل | حاويات صغيرة, قبعات الضغط المنخفض, القبعات الصناعية غير الثقيلة |
| بولي كلوريد الفينيل (بولي فينيل كلوريد) | صعب, مقاومة كيميائيا, أقل تحملاً للحرارة | زجاجات المختبر, قبعات صناعية غير عالية الحرارة |
| ABS (أكريلونتريل بوتادين ستايرين) | مقاومة عالية التأثير, مقاومة كيميائية معتدلة | قبعات عالية القوة للاستخدام الصناعي, تطبيقات مخصصة |
| جهاز كمبيوتر (البولي) | شفاف, مقاومة للتأثير | قبعات المراقبة, القبعات المتخصصة التي تتطلب الرؤية |
| السلطة الفلسطينية (مادة البولي أميد, نايلون) | قوة عالية, مقاومة للاهتراء | قبعات من النوع اللولبي, التطبيقات التي تتطلب جهدا ميكانيكيا |
| بوم (بولي أوكسي ميثيلين) | قوة عالية, احتكاك منخفض, مقاومة للاهتراء | قبعات ميكانيكية دقيقة, التطبيقات الصناعية المخصصة |
كيف يتم صناعة الأغطية البلاستيكية: عملية التصنيع خطوة بخطوة
إنتاج ذات جودة عالية قبعات بلاستيكية صناعية يتطلب الدقة, تناسق, ومجموعة من المواد والمعدات المتقدمة. إليك تفصيلًا خطوة بخطوة:
1. تحضير المواد
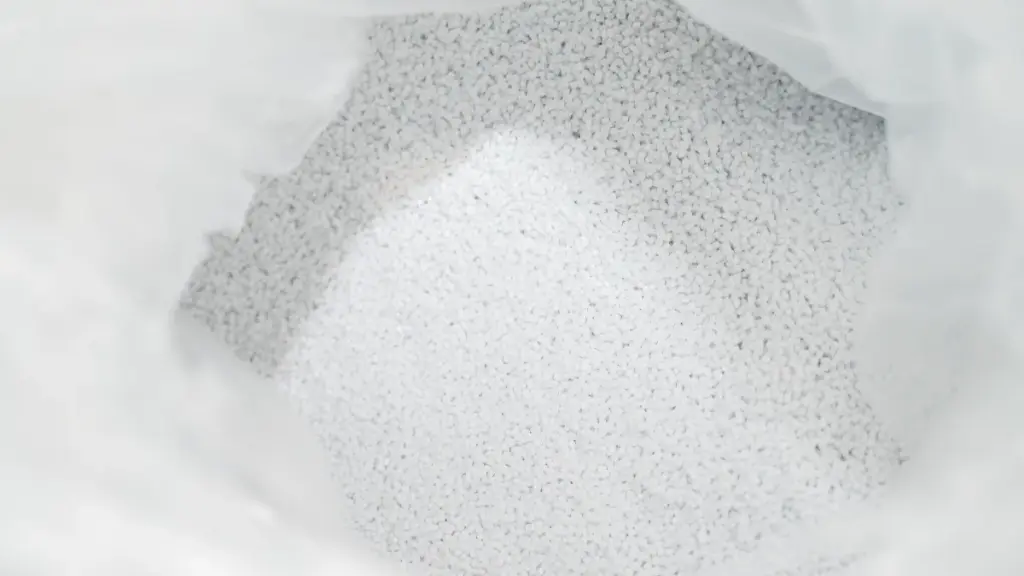

المواد الخام عالية الجودة هي أساس الأغطية البلاستيكية الصناعية المتينة. نحن نستخدم في المقام الأول مادة البولي إيثيلين الخام التي توفرها شركة سينوبك, وهو آمن للطعام ويوفر مقاومة كيميائية ثابتة, قوة, وأداء الختم. قبل صب, يتم مزج الكريات مع الأصبغة الرئيسية لتحقيق اللون المطلوب وقد تشتمل على مثبتات للأشعة فوق البنفسجية, عوامل مكافحة ساكنة, أو إضافات مضادة للشيخوخة حسب التطبيق. التجفيف المناسب يضمن تقليل الرطوبة, منع الفراغات أو نقاط الضعف أثناء القولبة, وإعداد المواد للتدفق الدقيق في القوالب.
2. عملية صب
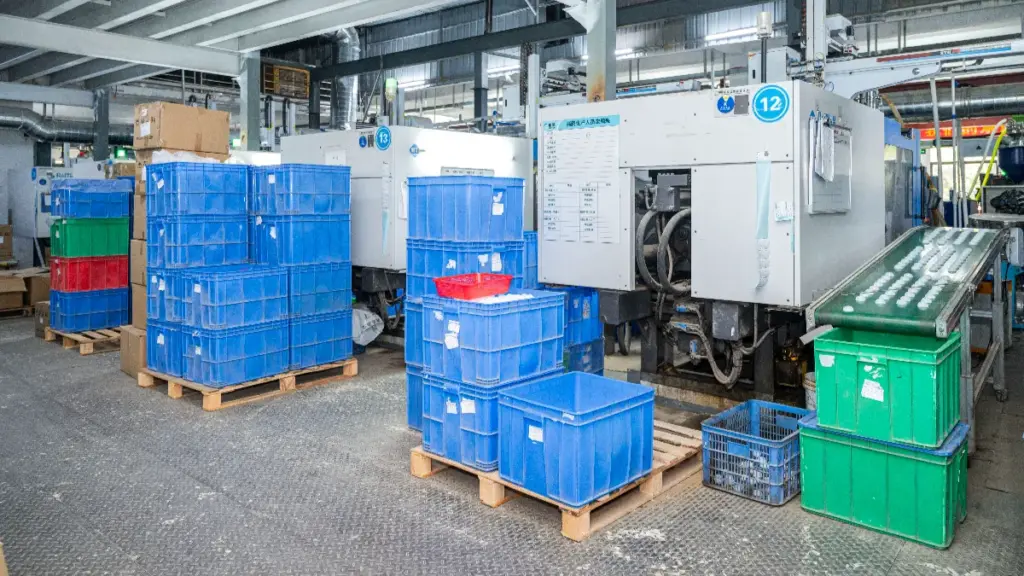

تعتبر عملية التشكيل هي الخطوة الأكثر أهمية في تصنيع الأغطية البلاستيكية الصناعية, لأنه يحدد شكل الغطاء, دقة الخيط, أداء الختم, والمتانة الشاملة. تستخدم خطوط الإنتاج لدينا آلات القولبة بالحقن الهايتية وتقنية قوالب العداء الساخن المتقدمة, ضمان التحكم الدقيق في درجة الحرارة, تدفق مستقر, وجودة متسقة عبر كل دفعة. في متضمنة, نحن نستخدم في المقام الأول قولبة الحقن والنفخ, هنا انهيار:
صب الحقن
يعتبر القولبة بالحقن هي الطريقة الأكثر شيوعًا ودقة لإنتاج الأغطية البلاستيكية الصناعية. إنه يركز على دقة ملء القالب, دقة الخيط, ونوعية السطح, مما يجعلها مثالية للأغطية المستخدمة في براميل الوقود, حاويات مواد التشحيم, وبراميل كيميائية.
نظرة عامة على العملية:
- تغذية & ذوبان: عادة ما يتم إذابة الحبيبات البلاستيكية إلى درجة حرارة 180-250 درجة مئوية.
- حقن: يتم حقن البلاستيك المصهور تحت ضغط 80-140 بار (مع ضغوط ذروة حوالي 200-230 ميجا باسكال) في تجويف القالب.
- تعبئة: تضمن تقنية العداء الساخن تدفقًا متساويًا للمواد, تشكيل خيوط دقيقة وأسطح الختم.
- تبريد: يتم الحفاظ على درجات حرارة القالب بين 20-60 درجة مئوية للتحكم في الانكماش والحفاظ على دقة الأبعاد.
- طرد: تستمر كل دورة حوالي 20-35 ثانية لكل تجويف, وبعد ذلك يتم إخراج الأغطية النهائية تلقائيًا للفحص.
صب النفخ
يتم استخدام قولبة النفخ لتصميمات الأغطية الأكبر أو المجوفة, حيث سمك الجدار موحد, توسعة باريس, والتحكم في التبريد من العوامل الرئيسية. إنها تناسب المنتجات التي تتطلب أغطية خفيفة الوزن لكنها قوية للحاويات الكبيرة أو الأغطية المتخصصة.
نظرة عامة على العملية:
- باريسون النتوء: يتم بثق البلاستيك الخام المنصهر في أنبوب مجوف يسمى أ باريسن عند درجات حرارة تتراوح بين 170-220 درجة مئوية, اعتمادًا على نوع الراتنج ومتطلبات سمك الجدار.
- لقط العفن: الباريسون محاط بنصفين من القالب مصنوعين من الفولاذ الدقيق, ضمان المحاذاة والتبريد الموحد.
- تضخم اقتصادي: يعمل الهواء المضغوط بضغط 5-10 بار على نفخ الباريسون, الضغط عليه بالتساوي على سطح القالب لتشكيل الشكل النهائي للغطاء.
- تبريد: يضمن تبريد القالب الذي يتم التحكم فيه عند درجة حرارة 15-40 درجة مئوية سماكة الجدار المتوازنة ويمنع التشوه.
- طرد: بمجرد مجموعات البلاستيك, يفتح القالب, ويتم إخراج الغطاء المشكل وتشذيبه قبل الفحص.
مع مجموعتنا من القوالب, مشتمل 64, 48, 32, 16, 8, و 4 تجاويف, يمكننا التعامل بمرونة مع كل من عمليات الإنتاج الكبيرة والصغيرة. اتصل بنا لمعرفة كيف يمكننا أن نقدم لك حلولاً كاملة لتناسب متطلباتك الصناعية.
3. التشذيب والتفتيش
بعد صب, المواد الزائدة, أو فلاش, تتم إزالتها باستخدام آلات التشذيب الآلية أو التشطيب اليدوي. يتم فحص كل غطاء بحثًا عن عيوب السطح, الشقوق, ودقة الأبعاد, بما في ذلك سلامة الخيط وملاءمته. وهذا يضمن أن القبعات تلبي التفاوتات الصارمة, منع التسربات والحفاظ على أداء الختم الموثوق به في ظل الظروف الصناعية.
4. إدخال الحشية
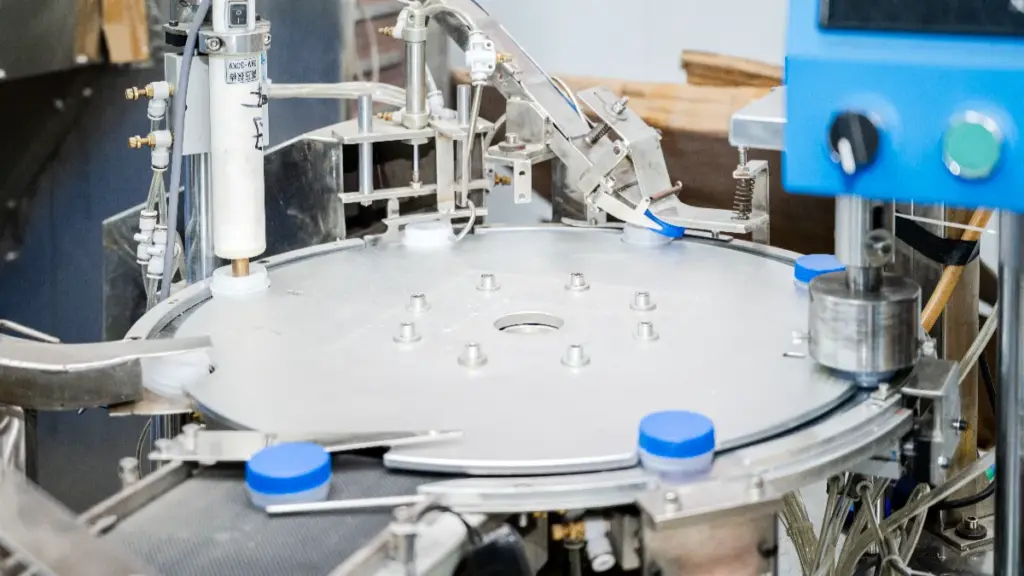

تشتمل العديد من الأغطية الصناعية على حشية, عادة ما تكون مصنوعة من المطاط أو رغوة EPE, لتعزيز الختم. يتم إدخال الحشيات يدويًا أو باستخدام معدات آلية, ضمان المحاذاة الصحيحة والقضاء على التجاعيد. تؤكد اختبارات التسرب الأولية فعالية الحشية, ضروري لحاويات المواد الكيميائية أو الوقود حيث يكون الختم الآمن إلزاميًا.
5. تخصيص
يمكن تخصيص القبعات بألوان مختلفة, الشعارات, أرقام الدفعة, أو رموز السلامة. نحن نستخدم طباعة الشاشة, ختم ساخن, نقل الحرارة, أو الترميز بالليزر حسب متطلبات المتانة والوضوح.
6. ضمان الجودة
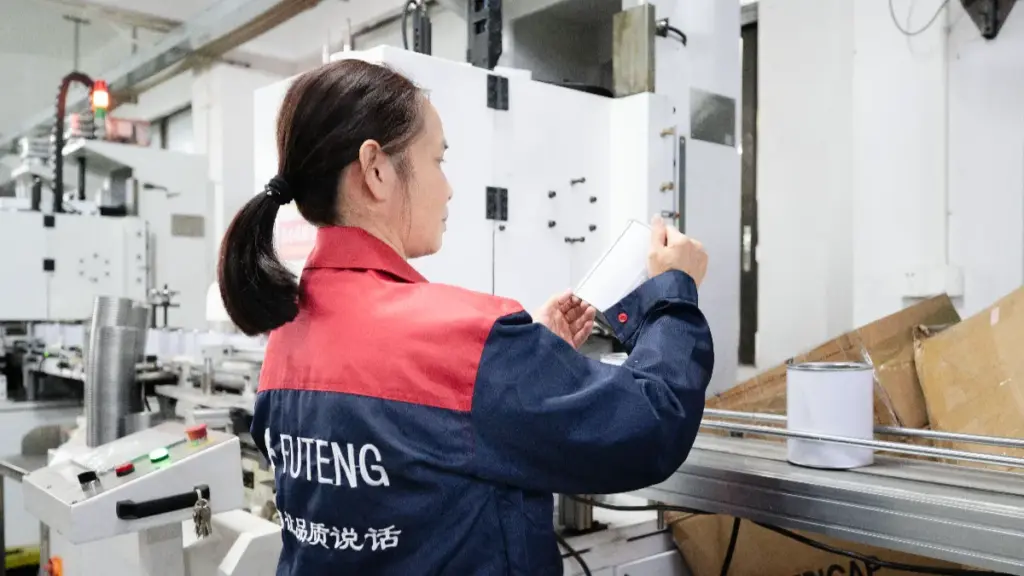

تخضع كل دفعة لاختبارات صارمة, بما في ذلك اختبارات الضغط والتسرب, تقييمات المقاومة الكيميائية, اختبارات السقوط, والتحقق من ملاءمة الخيط. تتحقق هذه الخطوات من أن الأغطية تحافظ على الأداء أثناء التخزين, ينقل, والاستخدام, تزويد العملاء الصناعيين الموثوقة, منتجات عالية الجودة.
7. التعبئة والتغليف والتسليم
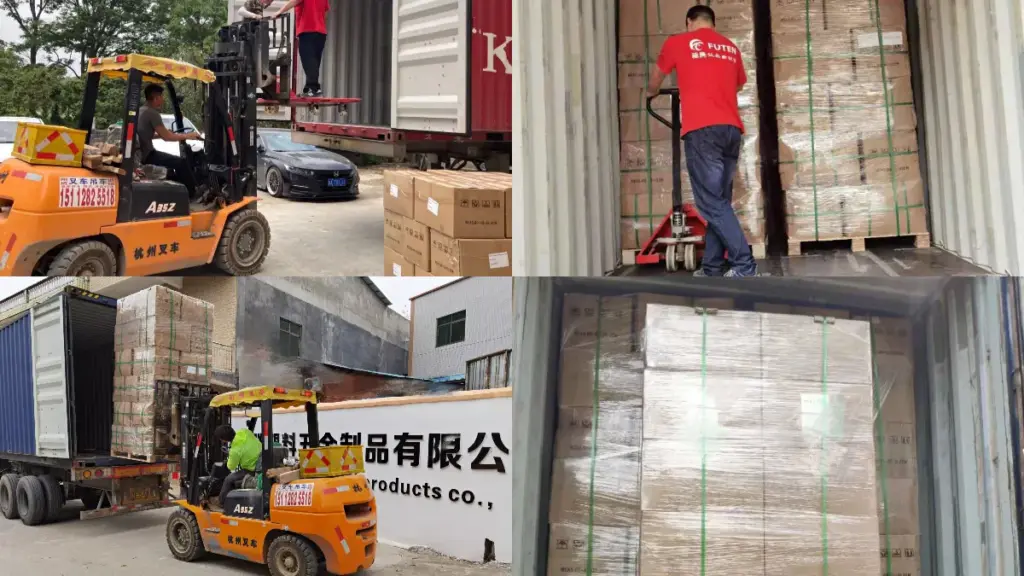

يتم فرز الأغطية المعتمدة وتعبئتها باستخدام أكياس البولي إيثيلين أو الفيلم المتقلص ووضعها في صناديق كرتونية عليها تواريخ الإنتاج وأرقام الدفعات.. يضمن هذا النهج المنهجي التسليم السلس, إدارة المخزون دقيقة, وإمكانية التتبع للعملاء.
مراقبة الجودة ومعايير السلامة في إنتاج الأغطية البلاستيكية
يجب أن تلبي الأغطية البلاستيكية الصناعية متطلبات الجودة والسلامة الصارمة لضمان سلامة الختم وموثوقية المواد.
- دقة الأبعاد: يتم الحفاظ على ميزات الخيط والختم في حدود ± 0.2 مم.
- اختبار المواد: يتم اختبار مواد HDPE وPP للتأكد من قوة الشد (HDPE 28-35 ميجا باسكال, ب 30-40 ميجا باسكال), مقاومة التأثير, والاستقرار الكيميائي.
- اختبارات الأداء: عزم الدوران, يسقط (1-2 م), واختبارات الضغط تؤكد القوة تحت الاستخدام الصناعي.
- شهادات المنتج: اعتمادا على التطبيق, قد تتوافق القبعات مع إدارة الغذاء والدواء, أستم, و/حصلت, أو معايير اختبار SGS لسلامة الأغذية, ينقل, والامتثال البيئي.
كيفية اختيار الشركة المصنعة للأغطية البلاستيكية المناسبة?
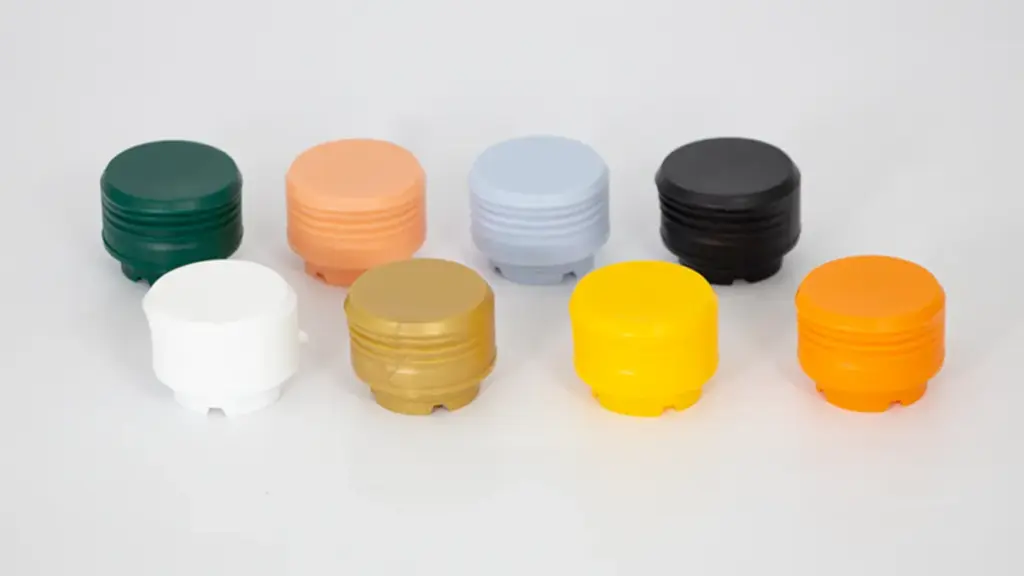

العمل مع الحق الشركة المصنعة للغطاء البلاستيكي يضمن أن الحاويات الخاصة بك مختومة بأمان, الامتثال للوائح, وتلبية توقعات المستخدمين النهائيين لديك. فيما يلي العوامل الرئيسية التي يجب مراعاتها:
- الخبرة والخبرة: شركة مصنعة تتمتع بسنوات من الخبرة في إنتاج أغطية الوقود, كيميائية, أو البراميل الصناعية سيكون لديها المعرفة للتعامل مع المتطلبات المعقدة.
- القدرة الإنتاجية: يحتاج العملاء ذوو الحجم الكبير إلى مورد يمكنه الحفاظ على إنتاج ثابت. على سبيل المثال, يمكن للمصنع الذي يحتوي على قوالب متعددة التجاويف وخطوط حقن آلية أن ينتج عشرات الآلاف من الأغطية يوميًا.
- خيارات التخصيص: غالبًا ما تتطلب التطبيقات الصناعية ميزات محددة مثل الأختام الواضحة للتلاعب, تصميمات مقاومة للأطفال, أو أغطية مقاومة للحرارة العالية. يجب أن تكون الشركة المصنعة قادرة على تخصيص التصاميم مع الحفاظ على الجودة.
- الاتساق وضمان الجودة: يجب أن يكون لدى الشركة المصنعة نظام قوي لمراقبة الجودة يغطي فحوصات الأبعاد, اختبارات المواد, وتقييمات الأداء. الشركات المصنعة مع ISO 9001 يُظهر المعتمدون التزامهم بالحفاظ على جودة المنتج المستقرة وتلبية مواصفات العملاء.
- التواصل والدعم: التواصل في الوقت المناسب, المشورة الفنية, ودعم ما بعد البيع ضروري. تُظهر الشركة المصنعة التي تقدم إرشادات مفصلة حول اختيار الغطاء وصيانته الاحترافية والموثوقية.
شريك مع شركة Futen للأغطية البلاستيكية الصناعية عالية الجودة
تأسست في 2015, لقد انتهى فوتن 15 سنوات من الخبرة في تقديم أغطية بلاستيكية متميزة و إغلاقات معدنية. منشأتنا تستثمر بكثافة في الإنتاج, تتميز بآلات الحقن الهايتية الرائدة في الصناعة وتقنية العداء الساخن المتقدمة. مع الأتمتة الكاملة والعمليات عالية الكفاءة, نحن ننتج ما يصل إلى 280 مليون حالة إغلاق سنويا. جميع منتجاتنا حاصلة على شهادة SGS لضمان الجودة والموثوقية المتسقة للحاويات الصناعية. إذا قمت بتصنيع الطبول الصناعية, علب الوقود, أو زجاجات مواد التشحيم ويبحثون عن أغطية عالية الجودة, يمكن لشركة Futen توفير الحلول التي تحتاجها.
تواصل معنا اليوم لمناقشة طلبك التالي وتأمين عمليات إغلاق عالية الجودة لعملك.
الأسئلة الشائعة
س1: هل يمكن استخدام المواد المعاد تدويرها للأغطية الصناعية?
أ1: بينما يمكن استخدام HDPE أو PP المعاد تدويره, تُفضل المواد البكر للتطبيقات الصناعية لضمان أقصى قدر من القوة, المقاومة الكيميائية, وأداء الختم. المواد المعاد تدويرها قد تقلل من قوة الشد بنسبة تصل إلى 20%, والتي يمكن أن تؤثر على موثوقية الغطاء.
Q2: كم من الوقت يستغرق إنتاج مجموعة من القبعات?
A2: تختلف أوقات الدورة حسب حجم الغطاء والمواد. قد يكون لغطاء HDPE القياسي مقاس 55 مم مدة دورة تتراوح من 15 إلى 20 ثانية, بينما قد يستغرق الغطاء الأكبر مقاس 100 مم من 30 إلى 40 ثانية. يتم تضمين وقت التبريد والتشذيب في هذه الدورات.
س3: ما هي العوامل التي تؤثر على أداء الحد الأقصى?
A3: اختيار المواد, دقة الخيط, تصميم القالب, ومراقبة الجودة كلها تؤثر على الأداء. التبريد غير السليم, اختيار المواد سيئة, أو يمكن أن تؤدي الخيوط غير الدقيقة إلى حدوث تسربات أو تشقق سابق لأوانه.
س 4: هل قبعاتك متوافقة مع الحاويات الصناعية القياسية؟?
A4: نعم, تم تصميم أغطيةنا لتتوافق مع مواصفات الأسطوانة والبرميل الشائعة. تتوفر أيضًا أحجام مخصصة وميزات خاصة عند الطلب.
س5: كيف يمكنك التأكد من المقاومة الكيميائية?
A5: نختار المواد بناءً على الخواص الكيميائية للمحتويات ونختبر كل دفعة للتأكد من توافقها. HDPE وPP مقاومان لمجموعة واسعة من الأحماض, قواعد, والمذيبات, مما يجعلها مثالية للاستخدام الصناعي.
















